So, you’re considering studying biomedical science, but you’re wondering just how hard it can be. It’s a valid concern and one that deserves a thorough response. As someone who has journeyed through the realm of biomedical science, I can assure you that it’s not overly complex. However, that doesn’t mean it’s a walk in the park either.
Biomedical science unearths a world of intricate biological processes and mechanisms, granting you the power to understand and explore the human body in all its glorious complexity.
One of the main challenges of the course, however, lies in the vast amount of content that needs to be memorised. From biochemistry to microbiology, there can be a lot to take in.
What Does a Biomedical Science Course Involve?

Each year
- Year 1: The first year typically serves as an introduction to the fundamental concepts and principles, giving you a strong base to build upon. You are also given an opportunity to get to know your class mates and faculty members.
- Exams in year one do not count towards your degree classification ususally.
- Year 2: This is where things start to get a bit more intense. Expect to dive deeper into the subject matters and cover topics such as cell morphology, biomedical lab techniques, and important genetics calculations. Exams count for a minority of the total degree classification, roughly 20%.
- In the second year, exams are mainly composed of essays which makes the second year a big jump in difficulty for many students.
- Year 3: Your final year is more advanced, requiring mastery of the topics covered in the previous years, and yes, more essays!
- In the final year, your exams will make up a majority of your final degree classification, with the final year research project making up most of your mark out of all the modules.
Thus, while the subject matter isn’t overwhelmingly complex, it’s the assessments, specifically the essays in years 2 and 3, that can make the degree seem somewhat tricky. As a result, you can’t bluff your way through year two or three in a biomedical science degree.
This is why there is generally a high dropout rate in many biomedical science degrees from year one to two – the workload which is already relatively high in year 1 gets harder in subsequent years.
But let me assure you, the effort is well worth it.
What is the typical workload for a biomedical science student?
As a prospective biomedical science student, it’s crucial to understand the nature of the programme. Many would agree that the only ‘easy’ period is the freshers week and perhaps the first few weeks of the first semester. During this time, you may feel a sense of calm before the storm, as the workload and pace gradually increase.
After the initial period, lectures start coming thick and fast, leaving you with a vast amount of content to absorb, from developmental biology to introductions to anatomy and physiology.
Now, here’s a common mistake that first-year students often make: attempting to learn everything and make notes from every lecture. While it might seem like a diligent approach, it can easily lead to an overwhelming backlog of content to review.
- The best strategy? Instead of trying to create notes from scratch for every lecture, use the lectures as a brief outline. This approach allows you to focus on understanding the key points and concepts.
- Then, supplement your knowledge with other well-formed resources. These resources can serve as the primary basis for your notes.
Following this strategy, you’re not left catching up every week with notes from ten different lectures. Instead, you’ll have a manageable workload and a deeper understanding of the essential content.
How Hard is Biomedical Science?

The level of difficulty encountered when studying a biomedical science degree is largely subjective and can vary greatly from one individual to another. While it is unarguably a challenging field of study, many factors can influence the experience and perception of difficulty. Let’s take a closer look.
- Interdisciplinary Nature: Biomedical science combines several fields of study, from biochemistry to genetics, pathology to microbiology. This interdisciplinary approach, while providing a holistic view of human health and disease, adds a layer of complexity and demands a broad understanding of a wide range of scientific disciplines.
- Ongoing Research: The biomedical science field is constantly evolving with ongoing research and emerging discoveries. Thus, students need to keep abreast of the latest developments, which may sometimes lead to uncertainty regarding the depth of learning required for each module.
- Multiple Concurrent Modules: A standard biomedical science programme typically involves studying multiple modules concurrently, which can present a challenging balancing act. Time management is crucial to navigate this aspect successfully.
Despite these challenges, a biomedical science degree remains an incredibly enriching and exciting venture for individuals passionate about science. The complexity and depth of subjects like biochemistry or DNA methylation can be captivating and stimulate curiosity, thereby reducing the perceived difficulty.
In conclusion, while biomedical science is not an easy degree to pursue, it presents an exciting learning opportunity. The difficulty level is largely what you make of it – a challenging yet rewarding journey for those with a keen interest in the scientific exploration of human health and disease.
What are the core subjects of a biomedical science degree?

Embarking on a journey to study biomedical science involves immersing yourself in a range of core subjects. These are the building blocks of the degree and are mandatory for all students enrolled. The core subjects often feature heavily in the first year of biomedical science.
- Anatomy and Physiology: This subject ensures you understand the structure and function of the human body at both a macroscopic and microscopic level.
- Nervous System: Here, you’ll delve into the complexities of the human brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Genetics: The study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in living organisms forms a critical part of biomedical science.
- Developmental Biology: This subject explores how organisms grow and develop.
- Microbiology: Microbiology focuses on the study of microscopic organisms such as bacteria and viruses.
- Molecular Biology: This subject delves into the interaction between the various systems of a cell, including DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis.
- Biochemistry: You’ll learn about the chemical processes related to living organisms.
From these core subjects stems a variety of optional specialist fields within the realm of biomedical science. These allow you to tailor your degree to your interests and career aspirations.
What skills do I need to succeed in a biomedical science degree?

For a successful journey in biomedical science, you’ll need to equip yourself with a range of skills. It’s not just about scientific knowledge, but also about how to apply that knowledge, analyse results, communicate findings, and work as part of a team. Let’s delve into these skills in more depth:
- Scientific understanding: This is a given. You’ll need a solid grounding in the biological sciences, as well as a good understanding of chemistry and, to a lesser extent, physics. Additionally, a good grasp of mathematics will be beneficial when it comes to analysing data.
- Research skills: Biomedical science is a research-intensive field. You’ll need to know how to design and conduct experiments, analyse data, interpret results, and draw conclusions. You’ll also need to be able to read and understand scientific literature.
- Analytical skills: The ability to think critically and analytically is paramount in biomedical science. You’ll often be required to solve complex problems, make connections between different pieces of information, and think outside the box.
- Communication skills: The ability to communicate scientific concepts and findings clearly and effectively is crucial. This includes both written and verbal communication. You’ll need to be able to write up your research in a clear and concise manner, and present your findings to others in a way that they can understand.
- Teamwork: Much of the work in biomedical science is done in teams. You’ll need to be able to work effectively with others, both within your own discipline and in multidisciplinary teams.
- Attention to detail: In the laboratory, even the smallest error can have significant consequences. You’ll need to be meticulous in your work, paying close attention to detail and ensuring accuracy in all you do.
- Time management: Biomedical science courses can be demanding, with a heavy workload and tight deadlines. You’ll need to be able to manage your time effectively, balancing your academic responsibilities with other commitments.
In addition to these, an inherent curiosity and a passion for understanding how the human body works are also beneficial in this field. If you find yourself genuinely interested in the subject matter, and motivated to learn and understand more, you’re already on the right path to succeeding in a biomedical science degree.
What are the career prospects after studying biomedical science?

After completing a degree in biomedical science, you’ll find that a world of opportunities opens up to you. Many graduates go on to work in a range of fascinating and challenging fields, where they can apply their knowledge and skills to real-world issues. But what exactly are these career prospects? Let’s delve a bit deeper.
One of the most common career paths for biomedical science graduates is in laboratory-based roles, either in research or in hospital settings. These roles typically involve conducting and analysing biological experiments, often with a focus on understanding and treating diseases. For example, you might find yourself investigating the genetic basis of cancer, or researching new treatments for neurological disorders.
Alternatively, some graduates opt to pursue further study in order to specialise in a particular area of biomedical science. This might involve undertaking a master’s degree or a PhD, after which you could work as a university researcher or lecturer. In these roles, you would be directly contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge, and potentially making breakthroughs that could have a significant impact on people’s lives.
Not all biomedical science graduates work in laboratories, however. Many find employment in a range of other settings, such as the pharmaceutical industry, where they might be involved in drug discovery and development. Others work in public health roles, helping to track, prevent and control diseases. Still others work in roles that combine science with other skills, such as science writing, patent law, or health policy.
And of course, a biomedical science degree can also serve as a stepping stone to a career in medicine. Many graduates go on to study medicine and become doctors, using their biomedical science background to provide them with a deeper understanding of the biological basis of disease.
So, no matter what your career aspirations might be, a biomedical science degree can provide you with a wide range of options. It’s a degree that equips you with a solid scientific foundation, as well as a host of transferrable skills that are highly valued by employers in many different sectors.
Is there a lot of memorization required in a biomedical science degree?
Yes, studying for a biomedical science degree does require a significant amount of memorisation. The volume of information that needs to be internalised can indeed be daunting. This covers a wide spectrum from the miniscule, such as the names of veins, arteries, and vessels serving each part of the body, to intricate biochemical pathways necessary for DNA post-translational modifications.
“Memorisation is an integral part of studying Biomedical Science, but don’t be daunted; there are strategies you can employ to make this more manageable.”
But fear not! While memorisation is a key component, there are effective techniques available to students to aid recall. One such approach is the use of mnemonics. This is a system that enhances memory by associating new information with previously known data through the use of patterns such as letters, ideas, or associations.
- Mnemonics: This is a powerful tool that can simplify the process of memorising complex concepts. For instance, one might create an acronym or a memorable phrase to remember the sequence of certain events or factors.
- Conceptual Frameworks: These are structures that represent the organisation of a concept or a topic. By understanding the bigger picture, you can more easily recall specific details.
In the final year, an assessment was conducted where a complicated research paper was assigned to each student by a professor, and a presentation would need to be delivered by the student over the duration of exactly 15 mins.
The aim was to assess a few things:
- Time management when delivering a presentation (as a lecturer has to do when delivering their lectures)
- Understanding of the entire research paper, themes, goals, findings, and methods used.
- Ability to simplify complex themes
Even such an assignment required a lot of memorisation – however this was undertaken in the final year and by then, reading 100s of research papers to memorise, understand and extract themes was already common place – so fear not!
How much laboratory work is involved in a biomedical science degree?
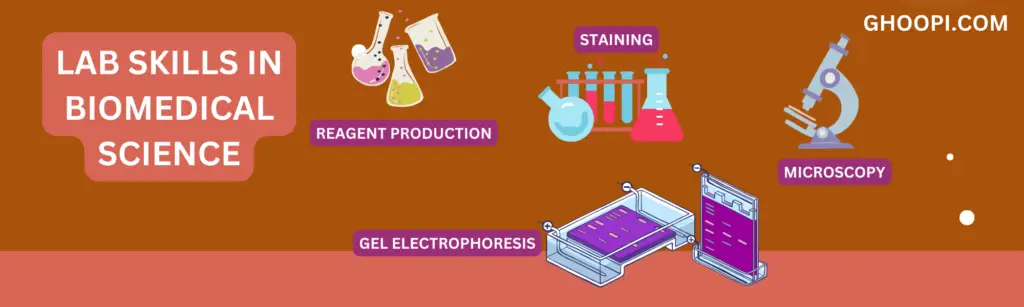
The study of biomedical science is inextricably linked with a significant amount of laboratory work. This is an undeniable reality of this course, and it’s one that you should be prepared for. In fact, it’s not uncommon for students to undertake a competency assessment at the end of their second year. This test ensures that they have mastered the essential lab skills that form the backbone of biomedical science. If a student cannot pass this assessment, they are not allowed to progress to the next academic year.
But fear not! The skills required for laboratory competency are taught right from the first year, ensuring that you have ample time to practice and perfect them.
Let’s review some of these vital lab skills:
- Microscopy: One of the first skills you’ll learn, including Koehler illumination, pulling focus, and viewing cells.
- Protein Staining: Critical for visualising specific proteins within a sample.
- Gel Electrophoresis: An important technique for separating DNA, RNA, or protein molecules.
- PCR & DNA Extraction: Fundamental techniques for studying genetic material.
- Pipetting: The ability to accurately measure and transfer small amounts of liquid is crucial.
- Cell Counts: Performing cell counts with a microscope and haemocytometer is a key skill in many lab procedures.
- Cell Morphology: Identifying differences between cell morphologies, both in tissue and in bacterial cells.
- Chemical Mixing & Dilution: The ability to mix chemicals and dilute appropriate concentrations of reagents, tested with a pH meter so there’s no room for error.
In conclusion, laboratory techniques form the cornerstone of biomedical science. They’re not just an optional extra, they’re a fundamental part of the course. So, if you’re considering pursuing a degree in this field, prepare yourself for a healthy dose of lab work!
What are the challenges of studying biomedical science?
Studying biomedical science is a rewarding yet challenging venture. Numerous factors might make the pursuit of this degree rather daunting to some students. Let’s delve into the specifics.
- Content Difficulty and Novelty: Biomedical science often introduces students to new and complex concepts. This is not a course where you’ll rehash high school subjects; it’s a field of study dealing with the intricate workings of living organisms.
- Interdisciplinary Blend: It’s a mix of multiple disciplines such as biology, medicine, and even a dash of mathematics. This blend can be overwhelming especially if one is not equally proficient in all the disciplines.
- Dependence on Memorisation: While some fields, like mathematics, build on basic principles, most of biomedical science relies on sheer memorisation. The vast amount of information to remember can be daunting.
- Fast-paced Learning: The quantity of material covered within two semesters is enormous. This fast-paced learning might prove challenging for those who prefer a more leisurely approach to education.
- Large Cohorts: Due to the popularity of the course, you might find yourself in a large class with limited opportunities for personalised attention from lecturers.
- Unforeseen Exam Questions: The nature of essay exams in this course means you won’t know the questions ahead of time, adding an element of unpredictability and stress.
- Research Paper Overload: There are numerous research papers to read and understand, often filled with complex subject-specific jargon. The comprehension and analysis of these papers can be overwhelming.
- Further Learning: Earning a biomedical science degree does not immediately make you a biomedical scientist. There’s more work to do and a portfolio to build, which entails further study and practical experience.
In summary, while studying biomedical science can be challenging, it is also an exciting field of study that offers a world of opportunities. Remember, every academic journey has its hurdles. The question is, are you ready for the challenge?
Is it necessary to have a background in biology to study biomedical science?
Deciding to embark on a degree in biomedical science is an exciting step, but you may wonder if it’s necessary to have a background in biology for this field of study. The answer isn’t as straightforward as you might think.
While a background in biology can be beneficial, it’s not strictly a must-have requirement. However, having a grasp of biology or chemistry at ‘A’ level is often one of the prerequisites for most universities.
- High School or ‘A’ Level Subjects: It is worth noting that most universities may require at least a ‘B/C’ in ‘A’ level biology or chemistry. This requirement is because these subjects provide a foundational understanding of the scientific principles on which biomedical science is based.
- Learning and Understanding: If you don’t have a solid background in biology, don’t let that deter you. The curriculum of a biomedical science degree is designed in a way that introduces students to new topics gradually. This approach ensures that even those with minimal biology backgrounds can keep up and understand the course material.
In conclusion, while a background in biology can provide a useful foundation for a biomedical science degree, it isn’t an absolute necessity. As long as you’re willing to learn and have a passion for the subject, you’ll find your path in this fascinating field.
Are there any prerequisites for studying biomedical science?

Most universities and colleges have specific entry requirements for a biomedical science degree. While these prerequisites may vary somewhat between institutions, there are some general prerequisites that are typically expected.
- A-Level Biology and Chemistry: Most institutions require A-levels in biology and chemistry, although some may accept a physical science instead of chemistry. It’s critical to check the specific requirements of each institution you’re interested in.
- Mathematics: Mathematics is usually not a mandatory prerequisite, but it can be highly beneficial, particularly for sections of the course that involve statistics and data analysis.
- English: Proof of proficiency in English is typically required, especially for international students. This could be through an IELTS or TOEFL exam score.
Beyond these academic prerequisites, a keen interest in the life sciences, a good work ethic, and strong problem-solving skills will certainly aid your studies in biomedical science. It’s also worth noting that some universities require an interview as part of the admission process. This is an opportunity for you to demonstrate your passion for the subject and your commitment to studying.
In short, while there are some standard prerequisites for studying biomedical science, the specific requirements can vary between institutions. Therefore, it’s essential to check the entry requirements of each university or college you’re interested in.
Tips for Succeeding in Biomedical Science

If you’ve decided to embark on a journey through biomedical science degree, you might be wondering how you can excel in such a challenging course. Fear not, for it is possible to succeed in this field with the right mix of dedication, passion, and the following tips:
Stay Organised
Biomedical science is a rigorous course that involves a lot of critical thinking and practical work. Being organised in your studies can help you manage your time effectively. Keep track of your assignments, labs, and lectures, and plan your study schedule accordingly.
Strengthen Your Foundation
As you delve into complex topics, having a strong foundation in basic biology, chemistry, and physics will make your studies easier. Spend time reinforcing these fundamental concepts as they form the backbone of biomedical science.
Engage in Practical Work
Biomedical science is not just about learning theories, it also requires a significant amount of laboratory work. Take your lab sessions seriously, as they provide you with the chance to apply what you’ve learnt in lectures and to gain hands-on experience that is crucial in this field.
Clarify Your Doubts
Don’t be afraid to ask questions if you don’t understand a concept. Professors, teaching assistants, and even your peers can be valuable resources when you’re struggling to understand a topic. Remember, the only silly question is the one that isn’t asked.
Stay Up-to-Date
Stay updated with the latest research and developments in the field of biomedical science. This not only enhances your knowledge but also keeps you engaged and motivated in your studies.
Network
this is a big one! For many students, especially the smart ones, they attempt to do everything on their own.
Networking with your professors, classmates, and professionals in the field can provide you with opportunities for internships, research projects, and even job prospects. Attend conferences, seminars, and workshops whenever you can.
Even if it’s just getting together to have a drink, go to the music room, or revise and make revision notes for an exam, making an effort to connect with someone will usually be a good step for success!
Take Care of Your Health
Lastly, but importantly, take care of your physical and mental health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can help you stay focused and energised. Don’t forget to take regular breaks to avoid burnout.
Remember, while the biomedical science degree can be challenging, it is also incredibly rewarding. With these tips, you’re well on your way to succeed in your academic journey and beyond.
Summary
Is studying for a biomedical science degree hard? The simple answer is – it can be. However, the level of difficulty often depends on a myriad of factors. Primarily, the approach one takes towards studying this complex subject significantly impacts the overall experience.
“The students who breeze through typically benefit from networking with peers, maintaining open communication with professors, and leaning on a support network to discuss assessments, upcoming exams, and tests.”
These students often go beyond the curriculum, engaging in vibrant discussions about the subject matter or just unwinding with their peers after a long day of studying. This collaborative approach can make the challenging content more digestible and the experience more enjoyable.
However, it’s worth noting that the students who typically find the course most challenging are those who attempt to undertake the degree in isolation. Without a network of friends or a good relationship with professors, they may find it hard to navigate through the complexity of the subject matter, since there is a lot to cover.
Key Success Factors in Studying Biomedical Science
- Networking with peers and participating in study groups
- Maintaining good communication with professors
- Developing a strong support network
- Seeking help when concepts are difficult to grasp
In summary, while studying biomedical science can be challenging, the difficulty can be mitigated by adopting a collaborative approach to learning, seeking help when needed, and cultivating a good relationship with both peers and professors.
![[MacOS Error] – Compressor does not support running in a macos virtual machine](https://cdn-0.ghoopi.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/img_6688-150x150.jpg)